About this database
Full-Entamoeba was constructed as a database of full-length cDNAs from a human parasite, Entamoeba histolytica and a reptilian parasite, E. invadens. Users can find genes of their interest that we can provide with in clone libraries for experimental purpose. Integrated tools enable the users to easily extract gene data by navigating them from multiple entry sites. Each entry is annotated with many types of biological data, which are linked to other databases.
Recently, we have added next generation sequence data, RNA-seq and TSS-seq, which provide
massive amount of transcriptomic infromation, deepening our understanding of transcripts from
both known and unknown genes.
Each type of core data is explained below.
Full-length cDNA
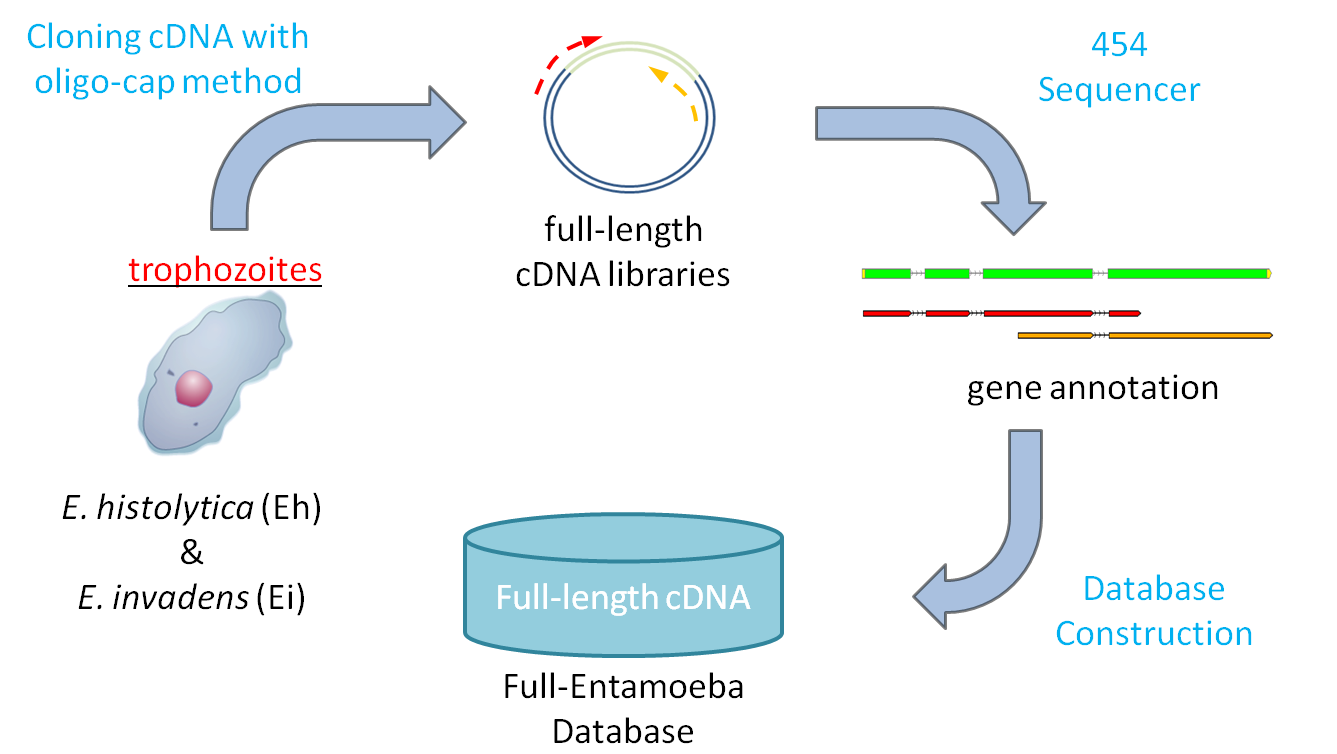
The full-length cDNA libraries were produced using oligo-capping method
from axenically cultivated trophozoites of
E. histolytica HM-IMSS and
E. invadens IP1.
For each of the two species, 5,000 of the clones were picked, sequenced at 5'and 3'end of
primers using 454 sequencer, and computationally processed(assembling, mapping, and annotating)
to construct the initial version of the database.
Obtained sequences are non-redundantly clustered into about 1,000 identical genes in each secies. Comparison with DDBL/Genbank/EMBL and the reference database of AmoebaDB shows that most of them match with known(e.i. experimentally or computationally inferred) gene structures although it is sure that the others contains several of possable novel genes. As expected from the reference data, 1/3 to 1/2 of the genes lack of functional annotation.
Preliminary analysis revealed that more than 95% of obtained gene structures had very short
5' untranslated region(5'UTR), ranging from 0 to 30 bp, and 3'UTRs were also thought to be
shorter than usual eukaryotic species.
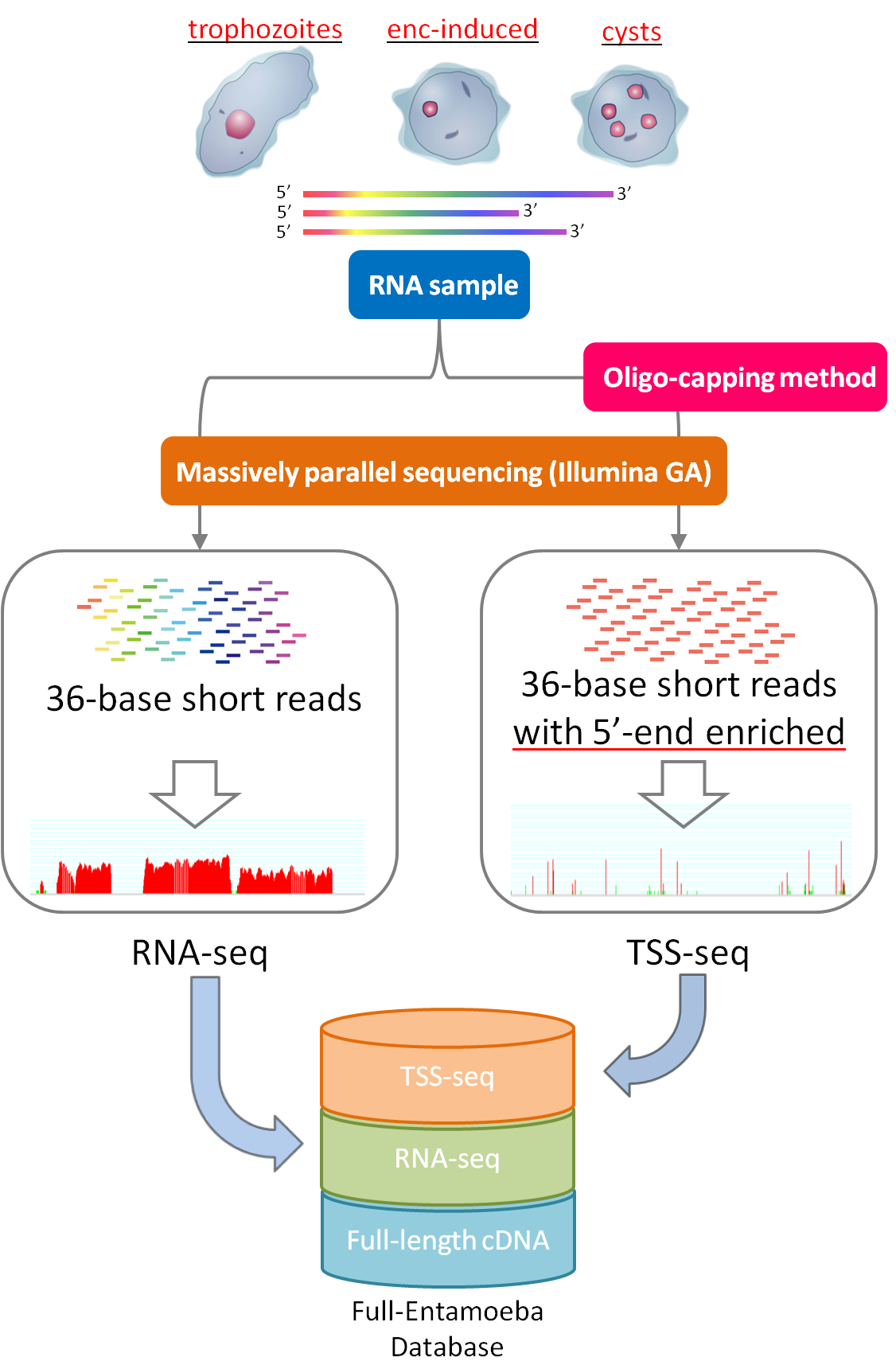
RNA-seq
A large collection of 36 bp short reads were sequenced using Illumina GA(RNA-seq). The RNA samples were prepared from torphozoites of E. histolytica HM-IMSS & E. invadens IP1 and cysts of E. invadens IP1 which had been generated by encystation induction. The "cysts" sample was obtained by being treated with sarkosyl solution to remove trophozoites.
Massive number of sequence reads can reveal detail structure for splicing variants of know genes, previously unpredicted genes, and non-coding RNA. The number of reads mapped on the region of full-length cDNAs or reference genes is digitally converted as thier expression levels which can be compared between trophozoites and cysts in E. invadens.
TSS-seq
Taking advantage of the oligo-capping method and massively paralell sequencing technology, comprehensive determination and characterization of transcription start sites (TSS) were performed in trophozoites of E. histolytica HM-IMSS & E. invadens IP1 and encystation-induced("enc-induced") of E. invadens. Please note that not as like "cysts" sample in RNA-seq, the "enc-induced" sample contains both trophozoites and individuals undergoing encystation because the sample was prepared right after inducton(to focus more on cyst-wall formation mechanism) and wasn't treated with sarkosyl solution.
TSS-seq is different with RNA-seq in that RNA sample is treated by oligo-capping method before going to sequnece step so that the output becomes exclusively enriched with 5'end of transcripts, and mapping TSS-seq tags on a reference genome appears as peak signal. Thus, compared with RNA-seq, the peak position explisitly tells where each transcript starts from. Moreover, differentiation at TSS can be more clearly analyzed than using full-length cDNA whose read number is not enough for statistical evaluation.